## 接口参数 **在 `Aggregator.py` 中**: - `global_merging=True`:是否在“global attention”阶段允许执行合并(默认允许) - `merging=0`:在第几个注意力 block 之后开始执行合并 实际用到 token merging 相关逻辑的地方只在于 global attention 中。相关逻辑调用在 `layers/attention.py` 中,部分函数实现在 `merging/merge.py` 中 ## `attention.py` 他这里还实现了分 chunk 计算。应该也有一部分对于最终提速的贡献。当然他论文是一点没说啊,但既然他这样干了,我们也没必要改回去吃这个哑巴亏。 具体实现流程: 1. 调用 `token_merge_bipartite2d` 返回一对 `(merge, unmerge)` 函数 2. 用 merge() 对 q、k、v 的“token 维度”进行merging(将一部分 src token 聚合到 dst token),得到更短的 $N_m$ 3. 用mering后的 q,k,v 做 scaled dot-product attention - 注意力输出后,再调用 unmerge() 把输出恢复到合并前的原始顺序与长度 ```python if global_merging is not None and global_merging in merge_num: generator = torch.Generator(device=x.device) generator.manual_seed(33) merge_ratio = 0.9 r = int(x.shape[1] * merge_ratio) m, u = token_merge_bipartite2d( x, self.patch_width, self.patch_height, 2, 2, r, False, generator, enable_protection=True, ) m_a, u_a = (m, u) B_q, H_q, N_q, D_q = q.shape q_merge_in = q.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) k_merge_in = k.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) v_merge_in = v.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) q_out, k_out, v_out = m_a( q_merge_in, mode="mean", extra_tensors=k_merge_in, extra_tensors_2=v_merge_in, ) del q_merge_in, k_merge_in, v_merge_in N_m = q_out.shape[1] q = q_out.reshape(B_q, N_m, H_q, D_q).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) k = k_out.reshape(B_q, N_m, H_q, D_q).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) v = v_out.reshape(B_q, N_m, H_q, D_q).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) del q_out, k_out, v_out N = N_m ``` ## `token_merge_barpartite()` ### 函数声明 ```plain 将标记分为源(src)组和目标(dst)组,并从源组向目标组合并r个标记。目标标记通过从每个(sx,sy)区域随机选择一个标记来选择。可选地,根据重要性得分保护顶部10%的标记不被合并。 参数: - metric [B, N, C]:用于相似度计算的张量,B = 批量大小,N = 标记数量,C = 特征维度 - w:图像宽度的标记数 - h:图像高度的标记数 - sx:目标在x维度的步长,必须能均匀整除w - sy:目标在y维度的步长,必须能均匀整除h - r:通过合并要移除的标记数量 - no_rand:如果为True,禁用随机性(仅使用左上角标记) - generator:如果no_rand为False且不为None时的随机数生成器 - enable_protection:如果为True,启用重要性保护特征 返回: - (merge, unmerge):两个函数,分别用于合并标记和恢复合并前状态 ``` Function call: ```python m, u = token_merge_bipartite2d( x, // tokens self.patch_width, self.patch_height, 2, //sx 2, //sy r, // r = int(x.shape[1] * merge_ratio) 即要“移除”并合并的 src token 数约占 90% False, generator, enable_protection=True, //实现上会均匀抽取 N 的 10% 的 token 索引为 protected_indices ) ``` ### 具体实现 论文中提到固定 `stride=10%N` 作为 protected tokens(保持 spatial consistency),首先实现于: ```python # 是否启用保护:当前实现为均匀抽样 N 的 10% 作为 protected 索引,防止被合并 if enable_protection: num_protected = int(N * 0.1) step = max(1, N // num_protected) # 均匀步进采样出受保护的索引列表 protected_indices = torch.arange(0, N, step, device=metric.device)[ :num_protected ] ``` 接下来开始划分 dst 和 src token、区分 frame 0 和 其他 frame ```python # idx_buffer_seq:长度为 N 的标记向量;-1 表示 dst,0 表示 src idx_buffer_seq = torch.zeros(N, device=metric.device, dtype=torch.int64) # hsy、wsx:分别是以 sy、sx 网格步幅划分后,每张图上的网格块数量(高、宽方向) hsy, wsx = h // sy, w // sx # Number of blocks within each image # 第一张图像(含 5 个特殊 token + 所有 patch)全部作为 dst 聚合目标 if num_imgs > 0: idx_buffer_seq[:tokens_per_img] = -1 # 因为 frame 0 的 tokens (including cam/reg) 都在 [0:tokens_per_img] # 其他 Frame: # 1) 每张图的 5 个特殊 token 标记为 dst # 2) 在每个 (sy, sx) 网格中选择 1 个 token 为 dst(其余默认 src) if num_imgs > 1: # 计算所有其它图像的 5 个特殊 token 的全局索引,并标记为 dst cls_indices = ( torch.arange(1, num_imgs, device=metric.device) * tokens_per_img ) cls_indices = cls_indices[:, None] + torch.arange(5, device=metric.device) idx_buffer_seq[cls_indices.flatten()] = -1 # 有效网格尺寸(避免越界):当 h 或 w 不能被 sy/sx 完整整除时,按可覆盖区域截断 effective_h = min(hsy * sy, h) effective_w = min(wsx * sx, w) effective_grid_size = effective_h * effective_w if no_rand: # 非随机:每个网格只选择固定(左上)位置为 dst。因为没有调用,遂掠过 else: # 随机:在每个 (sy, sx) 子网格里随机选一个索引作为 dst total_other_imgs = num_imgs - 1 all_rand_idx = torch.randint( sy * sx, size=(total_other_imgs, hsy, wsx), device=metric.device, generator=generator, ) # scatter_src 为 -1,用于把被选中的网格位置标记为 dst scatter_src = -torch.ones( total_other_imgs, hsy, wsx, device=metric.device, dtype=torch.int64 ) # idx_buffer_batch 的最后一维大小为 sy*sx,代表每个网格内的所有位置; # 先在该维度上做 scatter,把随机选中的位置置为 -1(dst),其余保持 0(src) idx_buffer_batch = torch.zeros( total_other_imgs, hsy, wsx, sy * sx, device=metric.device, dtype=torch.int64, ) idx_buffer_batch.scatter_( dim=3, index=all_rand_idx.unsqueeze(-1), src=scatter_src.unsqueeze(-1), ) # 将每个网格的 sy*sx 展开成二维平面,并按 (H, W) 的顺序重排(transpose + reshape) idx_buffer_batch = ( idx_buffer_batch.view(total_other_imgs, hsy, wsx, sy, sx) .transpose(2, 3) .reshape(total_other_imgs, hsy * sy, wsx * sx) ) # 将每张图对应的二维标记平面(-1 或 0)批量写入到全局 idx_buffer_seq 中对应的 patch 区域 # 注意 grid_start 跳过了前 5 个特殊 token for i in range(total_other_imgs): img_idx = i + 1 grid_start = img_idx * tokens_per_img + 5 flat_view = idx_buffer_batch[ i, :effective_h, :effective_w ].flatten() idx_buffer_seq[grid_start : grid_start + effective_grid_size] = ( flat_view ) ``` **说结论:如果要修改的话,可以仿照这一段的写法。可以是实现一个函数返回一个 indicies ,表示这些位置都需要设成 dst tokens。即现在代码的:`scatter_src`** 最后这一部分简单说一下几个不太会用的点: - `_scatter` : 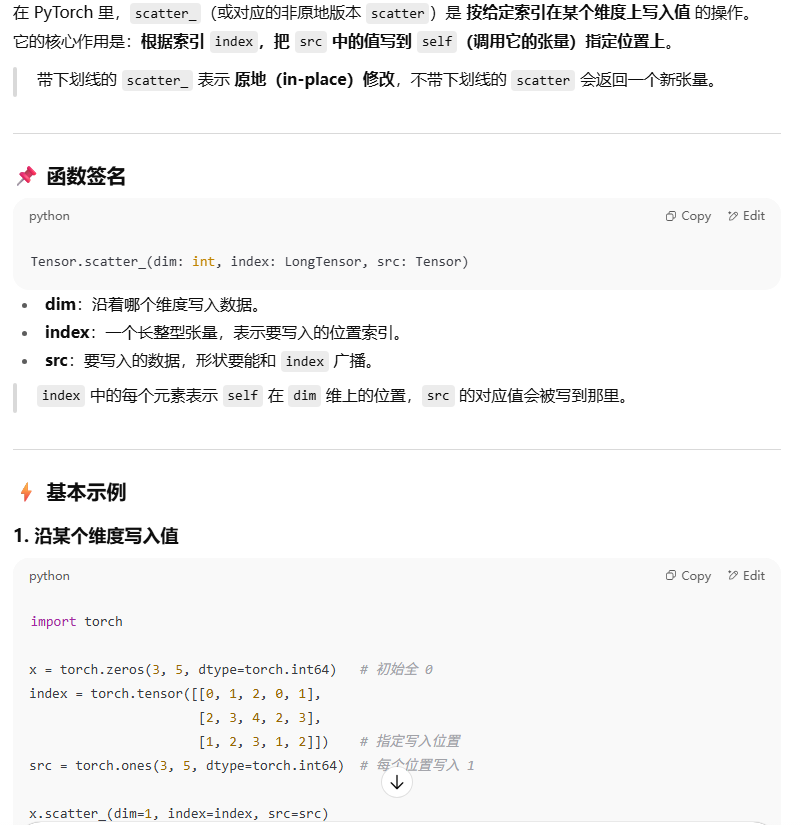 然后过度一下,拼接一下 dst token 和 src token,并且判断是否需要使用 protection 机制。最后记录 dst/src token 分别的数量。 ```python # 通过 argsort 将 -1(dst)排在前面,0(src)排在后面,得到两侧的索引集合 rand_idx = idx_buffer_seq.reshape(1, -1, 1).argsort(dim=1) num_dst_orig = int((idx_buffer_seq == -1).sum()) # 原始 src 与 dst 的索引切分(形状 [1, K, 1]) a_idx_orig = rand_idx[:, num_dst_orig:, :] b_idx_orig = rand_idx[:, :num_dst_orig, :] a_idx = a_idx_orig b_idx = b_idx_orig # 若启用保护,构造受保护索引的形状以适配 gather([1, P, 1]) if enable_protection: protected_idx = protected_indices.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(-1) num_protected_actual = protected_idx.shape[1] else: protected_idx = None num_protected_actual = 0 # 记录两侧的数量,便于后续分割与 scatter/gather num_src = a_idx.shape[1] num_dst = b_idx.shape[1] # 内部辅助函数:根据 a_idx/b_idx/protected_idx 将输入 x 分割为 src/dst/(protected) def split(x): C = x.shape[-1] if enable_protection: src = gather(x, dim=1, index=a_idx.expand(B, num_src, C)) dst = gather(x, dim=1, index=b_idx.expand(B, num_dst, C)) protected = gather( x, dim=1, index=protected_idx.expand(B, num_protected_actual, C) ) return src, dst, protected else: src = gather(x, dim=1, index=a_idx.expand(B, num_src, C)) dst = gather(x, dim=1, index=b_idx.expand(B, num_dst, C)) return src, dst ``` 然后开始计算 src 和 dst token 之间的 similarity 以及对应的 dst token 的 index ```python # 创建未初始化的张量用于存储每个 src 的最大相似度与对应的 dst 索引 node_max = torch.empty(B, num_src_actual, device=a.device, dtype=a.dtype) node_idx = torch.empty(B, num_src_actual, device=a.device, dtype=torch.long) # 将 dst 转置为 [B, C, num_dst],用于 a 与 bmm 计算 b_transposed = b.transpose(-1, -2) # 分块计算每个 src 的最大相似度与 argmax dst node_max, node_idx = fast_similarity_chunks(a, b_transposed, chunk_size) # 按最大相似度由大到小排序,得到 src 的优先级队列(edge_idx) edge_idx = node_max.argsort(dim=-1, descending=True)[..., None] ``` similarity 的代码等会儿讲。 最后保存结果: **如果要修改构图 or merging 的方式,则应该开始修改接下来这一段代码** ```python # 若启用保护:过滤掉属于保护集合的 src,保证这些 token 不被合并 if enable_protection: src_indices = a_idx[0, :, 0] protected_mask_src = torch.isin(src_indices, protected_indices) edge_flat = edge_idx[0, :, 0] # 仅保留未被保护的边 valid_mask = ~protected_mask_src[edge_flat] # 取反 valid_edges = edge_flat[valid_mask] valid_count = valid_edges.shape[0] r_actual = min(r, valid_count) # 根据 r_actual 切分:前 r_actual 为待合并 src,后面为未合并 src unm_idx = valid_edges[r_actual:].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(-1) src_idx = valid_edges[:r_actual].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(-1) else: # 无保护时,直接用 edge_idx 切分;前 r 为待合并 src,其余为未合并 src unm_idx = edge_idx[..., r:, :] src_idx = edge_idx[..., :r, :] r_actual = r # 为每个待合并的 src 查出它指向的 argmax dst 索引 dst_idx = gather(node_idx[..., None], dim=-2, index=src_idx) # 用 r_actual 回写 r,便于后续一致性(extra_tensors 同步) r = r_actual ``` ### 最终参与 `merge` 的 tensor 注意到,这里实际上最后出来了三个存 token 的 tensor:`src`, `umn`, `dst` 如果 `enable_protection = True`,则还会有一个额外的 `protected` tensor - `src` 对应要 merge 掉的 tensor - `umn` 对应:当前的合并比例是 $r$,那么剩下的 $N \times (1 - r)$ 个 tensor 就是不合并的,存储在 `umn` 中 - `dst` 对应:`src` token 要合并到 `dst` token 上 ## `merge()` ### 函数声明 ```python # 定义合并函数:把选中的 src 汇聚到对应的 dst(默认 reduce=mean),并返回拼接结果 def merge( x: torch.Tensor, mode: str = "mean", extra_tensors=None, # 额外同步合并的 tensor,保证后续 q@k 的序列长度一致。 extra_tensors_2=None, # 额外同步合并的 tensor 2,同上 ) -> Union[ torch.Tensor, Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], ]: ``` Function call (in `attention.py`): ```python q_merge_in = q.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) k_merge_in = k.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) v_merge_in = v.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) q_out, k_out, v_out = m_a( q_merge_in, mode="mean", extra_tensors=k_merge_in, extra_tensors_2=v_merge_in, ) ``` ### 具体实现 ```python # 按与 metric 相同的分割策略拆分 x if enable_protection: src, dst, protected = split(x) else: src, dst = split(x) n, t1, c = src.shape # 未合并的 src:根据 unm_idx 取出保留的 src 片段 unm_len = unm_idx.shape[1] unm = gather(src, dim=-2, index=unm_idx.expand(n, unm_len, c)) # 待合并的 src:根据 src_idx 选出前 r 个 src_len = src_idx.shape[1] src = gather(src, dim=-2, index=src_idx.expand(n, src_len, c)) # 将待合并的 src 聚合到对应的 dst;mode 默认为 mean,可改为 sum 等 dst = dst.scatter_reduce(-2, dst_idx.expand(n, src_len, c), src, reduce=mode) ``` 后面 `extra_tensors / extra_tensors1` 的流程是一样的。 ## `unmerge()` ```python # 先按顺序切分短序列:未合并 src(unm)、聚合后 dst、(可选)protected unm_len = unm_idx.shape[1] dst_len = num_dst src_len = src_idx.shape[1] unm = x[..., :unm_len, :] dst = x[..., unm_len : unm_len + dst_len, :] if enable_protection: protected = x[ ..., unm_len + dst_len : unm_len + dst_len + num_protected_actual, : ] # 用 dst 的聚合结果反向还原被合并的 src:根据 dst_idx 把 dst 拷回合适位置 _, _, c = unm.shape src = gather(dst, dim=-2, index=dst_idx.expand(B, src_len, c)) # 准备完整输出,并逐块 scatter 到原始索引位置 out = torch.zeros(B, N, c, device=x.device, dtype=x.dtype) # 1) 把 dst 放回原来的 b_idx(目标侧)位置 out.scatter_(dim=-2, index=b_idx.expand(B, num_dst, c), src=dst) # 2) 把未合并的 src 放回 a_idx 对应的 unm_idx 位置 out.scatter_( dim=-2, index=gather( a_idx.expand(B, a_idx.shape[1], 1), dim=1, index=unm_idx ).expand(B, unm_len, c), src=unm, ) # 3) 把被合并的 src(从 dst 反向恢复出来的片段)放回 a_idx 对应的 src_idx 位置 out.scatter_( dim=-2, index=gather( a_idx.expand(B, a_idx.shape[1], 1), dim=1, index=src_idx ).expand(B, src_len, c), src=src, ) # 4) 若启用保护,将 protected 片段 scatter 回 protected_idx 对应位置 if enable_protection: out.scatter_( dim=-2, index=protected_idx.expand(B, num_protected_actual, c), src=protected, ) return out ``` ## `fast_similarity_chunks()` ### 函数声明 ```python def fast_similarity_chunks( a: torch.Tensor, b_transposed: torch.Tensor, chunk_size: int ) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]: ``` Function call: ```python node_max, node_idx = fast_similarity_chunks(a, b_transposed, chunk_size) ``` ### 具体实现 注:`torch.bmm` 的全称是 **batch matrix-matrix product**,也就是 **批量矩阵乘法**。它一次性对一批(batch)里的多个矩阵做乘法运算。 - 输入:两个三维张量 `input` 和 `mat2` - 形状分别是 `(b, n, m)` 和 `(b, m, p)` - 输出:三维张量,形状是 `(b, n, p)` 其中 **`b`** 表示 batch size,也就是一批里有多少个矩阵要相乘。 每个 batch 内对应位置的矩阵会被相乘。 核心代码: ```python # Process in chunks for i in range(0, num_src, chunk_size): end_i = min(i + chunk_size, num_src) a_chunk = a_bf16[:, i:end_i, :] # [B, chunk_size, C] scores_chunk = torch.bmm(a_chunk, b_transposed_bf16) # 由于外层已对 a、b 做 L2 归一化,点积近似余弦相似度 chunk_max_bf16, chunk_idx = torch.max(scores_chunk, dim=2) # 在每个 src 行上找出最大值及其列索引(对应某个 dst chunk_max = chunk_max_bf16.to(original_dtype) node_max[:, i:end_i] = chunk_max node_idx[:, i:end_i] = chunk_idx return node_max, node_idx ``` ## 总结 1. 如果考虑要修改 protected token 的代码,那么所有 `enable_protection` 的代码都应该被考虑修改 2. ... Loading... ## 接口参数 **在 `Aggregator.py` 中**: - `global_merging=True`:是否在“global attention”阶段允许执行合并(默认允许) - `merging=0`:在第几个注意力 block 之后开始执行合并 实际用到 token merging 相关逻辑的地方只在于 global attention 中。相关逻辑调用在 `layers/attention.py` 中,部分函数实现在 `merging/merge.py` 中 ## `attention.py` 他这里还实现了分 chunk 计算。应该也有一部分对于最终提速的贡献。当然他论文是一点没说啊,但既然他这样干了,我们也没必要改回去吃这个哑巴亏。 具体实现流程: 1. 调用 `token_merge_bipartite2d` 返回一对 `(merge, unmerge)` 函数 2. 用 merge() 对 q、k、v 的“token 维度”进行merging(将一部分 src token 聚合到 dst token),得到更短的 $N_m$ 3. 用mering后的 q,k,v 做 scaled dot-product attention - 注意力输出后,再调用 unmerge() 把输出恢复到合并前的原始顺序与长度 ```python if global_merging is not None and global_merging in merge_num: generator = torch.Generator(device=x.device) generator.manual_seed(33) merge_ratio = 0.9 r = int(x.shape[1] * merge_ratio) m, u = token_merge_bipartite2d( x, self.patch_width, self.patch_height, 2, 2, r, False, generator, enable_protection=True, ) m_a, u_a = (m, u) B_q, H_q, N_q, D_q = q.shape q_merge_in = q.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) k_merge_in = k.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) v_merge_in = v.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) q_out, k_out, v_out = m_a( q_merge_in, mode="mean", extra_tensors=k_merge_in, extra_tensors_2=v_merge_in, ) del q_merge_in, k_merge_in, v_merge_in N_m = q_out.shape[1] q = q_out.reshape(B_q, N_m, H_q, D_q).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) k = k_out.reshape(B_q, N_m, H_q, D_q).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) v = v_out.reshape(B_q, N_m, H_q, D_q).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) del q_out, k_out, v_out N = N_m ``` ## `token_merge_barpartite()` ### 函数声明 ```plain 将标记分为源(src)组和目标(dst)组,并从源组向目标组合并r个标记。目标标记通过从每个(sx,sy)区域随机选择一个标记来选择。可选地,根据重要性得分保护顶部10%的标记不被合并。 参数: - metric [B, N, C]:用于相似度计算的张量,B = 批量大小,N = 标记数量,C = 特征维度 - w:图像宽度的标记数 - h:图像高度的标记数 - sx:目标在x维度的步长,必须能均匀整除w - sy:目标在y维度的步长,必须能均匀整除h - r:通过合并要移除的标记数量 - no_rand:如果为True,禁用随机性(仅使用左上角标记) - generator:如果no_rand为False且不为None时的随机数生成器 - enable_protection:如果为True,启用重要性保护特征 返回: - (merge, unmerge):两个函数,分别用于合并标记和恢复合并前状态 ``` Function call: ```python m, u = token_merge_bipartite2d( x, // tokens self.patch_width, self.patch_height, 2, //sx 2, //sy r, // r = int(x.shape[1] * merge_ratio) 即要“移除”并合并的 src token 数约占 90% False, generator, enable_protection=True, //实现上会均匀抽取 N 的 10% 的 token 索引为 protected_indices ) ``` ### 具体实现 论文中提到固定 `stride=10%N` 作为 protected tokens(保持 spatial consistency),首先实现于: ```python # 是否启用保护:当前实现为均匀抽样 N 的 10% 作为 protected 索引,防止被合并 if enable_protection: num_protected = int(N * 0.1) step = max(1, N // num_protected) # 均匀步进采样出受保护的索引列表 protected_indices = torch.arange(0, N, step, device=metric.device)[ :num_protected ] ``` 接下来开始划分 dst 和 src token、区分 frame 0 和 其他 frame ```python # idx_buffer_seq:长度为 N 的标记向量;-1 表示 dst,0 表示 src idx_buffer_seq = torch.zeros(N, device=metric.device, dtype=torch.int64) # hsy、wsx:分别是以 sy、sx 网格步幅划分后,每张图上的网格块数量(高、宽方向) hsy, wsx = h // sy, w // sx # Number of blocks within each image # 第一张图像(含 5 个特殊 token + 所有 patch)全部作为 dst 聚合目标 if num_imgs > 0: idx_buffer_seq[:tokens_per_img] = -1 # 因为 frame 0 的 tokens (including cam/reg) 都在 [0:tokens_per_img] # 其他 Frame: # 1) 每张图的 5 个特殊 token 标记为 dst # 2) 在每个 (sy, sx) 网格中选择 1 个 token 为 dst(其余默认 src) if num_imgs > 1: # 计算所有其它图像的 5 个特殊 token 的全局索引,并标记为 dst cls_indices = ( torch.arange(1, num_imgs, device=metric.device) * tokens_per_img ) cls_indices = cls_indices[:, None] + torch.arange(5, device=metric.device) idx_buffer_seq[cls_indices.flatten()] = -1 # 有效网格尺寸(避免越界):当 h 或 w 不能被 sy/sx 完整整除时,按可覆盖区域截断 effective_h = min(hsy * sy, h) effective_w = min(wsx * sx, w) effective_grid_size = effective_h * effective_w if no_rand: # 非随机:每个网格只选择固定(左上)位置为 dst。因为没有调用,遂掠过 else: # 随机:在每个 (sy, sx) 子网格里随机选一个索引作为 dst total_other_imgs = num_imgs - 1 all_rand_idx = torch.randint( sy * sx, size=(total_other_imgs, hsy, wsx), device=metric.device, generator=generator, ) # scatter_src 为 -1,用于把被选中的网格位置标记为 dst scatter_src = -torch.ones( total_other_imgs, hsy, wsx, device=metric.device, dtype=torch.int64 ) # idx_buffer_batch 的最后一维大小为 sy*sx,代表每个网格内的所有位置; # 先在该维度上做 scatter,把随机选中的位置置为 -1(dst),其余保持 0(src) idx_buffer_batch = torch.zeros( total_other_imgs, hsy, wsx, sy * sx, device=metric.device, dtype=torch.int64, ) idx_buffer_batch.scatter_( dim=3, index=all_rand_idx.unsqueeze(-1), src=scatter_src.unsqueeze(-1), ) # 将每个网格的 sy*sx 展开成二维平面,并按 (H, W) 的顺序重排(transpose + reshape) idx_buffer_batch = ( idx_buffer_batch.view(total_other_imgs, hsy, wsx, sy, sx) .transpose(2, 3) .reshape(total_other_imgs, hsy * sy, wsx * sx) ) # 将每张图对应的二维标记平面(-1 或 0)批量写入到全局 idx_buffer_seq 中对应的 patch 区域 # 注意 grid_start 跳过了前 5 个特殊 token for i in range(total_other_imgs): img_idx = i + 1 grid_start = img_idx * tokens_per_img + 5 flat_view = idx_buffer_batch[ i, :effective_h, :effective_w ].flatten() idx_buffer_seq[grid_start : grid_start + effective_grid_size] = ( flat_view ) ``` **说结论:如果要修改的话,可以仿照这一段的写法。可以是实现一个函数返回一个 indicies ,表示这些位置都需要设成 dst tokens。即现在代码的:`scatter_src`** 最后这一部分简单说一下几个不太会用的点: - `_scatter` :  然后过度一下,拼接一下 dst token 和 src token,并且判断是否需要使用 protection 机制。最后记录 dst/src token 分别的数量。 ```python # 通过 argsort 将 -1(dst)排在前面,0(src)排在后面,得到两侧的索引集合 rand_idx = idx_buffer_seq.reshape(1, -1, 1).argsort(dim=1) num_dst_orig = int((idx_buffer_seq == -1).sum()) # 原始 src 与 dst 的索引切分(形状 [1, K, 1]) a_idx_orig = rand_idx[:, num_dst_orig:, :] b_idx_orig = rand_idx[:, :num_dst_orig, :] a_idx = a_idx_orig b_idx = b_idx_orig # 若启用保护,构造受保护索引的形状以适配 gather([1, P, 1]) if enable_protection: protected_idx = protected_indices.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(-1) num_protected_actual = protected_idx.shape[1] else: protected_idx = None num_protected_actual = 0 # 记录两侧的数量,便于后续分割与 scatter/gather num_src = a_idx.shape[1] num_dst = b_idx.shape[1] # 内部辅助函数:根据 a_idx/b_idx/protected_idx 将输入 x 分割为 src/dst/(protected) def split(x): C = x.shape[-1] if enable_protection: src = gather(x, dim=1, index=a_idx.expand(B, num_src, C)) dst = gather(x, dim=1, index=b_idx.expand(B, num_dst, C)) protected = gather( x, dim=1, index=protected_idx.expand(B, num_protected_actual, C) ) return src, dst, protected else: src = gather(x, dim=1, index=a_idx.expand(B, num_src, C)) dst = gather(x, dim=1, index=b_idx.expand(B, num_dst, C)) return src, dst ``` 然后开始计算 src 和 dst token 之间的 similarity 以及对应的 dst token 的 index ```python # 创建未初始化的张量用于存储每个 src 的最大相似度与对应的 dst 索引 node_max = torch.empty(B, num_src_actual, device=a.device, dtype=a.dtype) node_idx = torch.empty(B, num_src_actual, device=a.device, dtype=torch.long) # 将 dst 转置为 [B, C, num_dst],用于 a 与 bmm 计算 b_transposed = b.transpose(-1, -2) # 分块计算每个 src 的最大相似度与 argmax dst node_max, node_idx = fast_similarity_chunks(a, b_transposed, chunk_size) # 按最大相似度由大到小排序,得到 src 的优先级队列(edge_idx) edge_idx = node_max.argsort(dim=-1, descending=True)[..., None] ``` similarity 的代码等会儿讲。 最后保存结果: **如果要修改构图 or merging 的方式,则应该开始修改接下来这一段代码** ```python # 若启用保护:过滤掉属于保护集合的 src,保证这些 token 不被合并 if enable_protection: src_indices = a_idx[0, :, 0] protected_mask_src = torch.isin(src_indices, protected_indices) edge_flat = edge_idx[0, :, 0] # 仅保留未被保护的边 valid_mask = ~protected_mask_src[edge_flat] # 取反 valid_edges = edge_flat[valid_mask] valid_count = valid_edges.shape[0] r_actual = min(r, valid_count) # 根据 r_actual 切分:前 r_actual 为待合并 src,后面为未合并 src unm_idx = valid_edges[r_actual:].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(-1) src_idx = valid_edges[:r_actual].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(-1) else: # 无保护时,直接用 edge_idx 切分;前 r 为待合并 src,其余为未合并 src unm_idx = edge_idx[..., r:, :] src_idx = edge_idx[..., :r, :] r_actual = r # 为每个待合并的 src 查出它指向的 argmax dst 索引 dst_idx = gather(node_idx[..., None], dim=-2, index=src_idx) # 用 r_actual 回写 r,便于后续一致性(extra_tensors 同步) r = r_actual ``` ### 最终参与 `merge` 的 tensor 注意到,这里实际上最后出来了三个存 token 的 tensor:`src`, `umn`, `dst` 如果 `enable_protection = True`,则还会有一个额外的 `protected` tensor - `src` 对应要 merge 掉的 tensor - `umn` 对应:当前的合并比例是 $r$,那么剩下的 $N \times (1 - r)$ 个 tensor 就是不合并的,存储在 `umn` 中 - `dst` 对应:`src` token 要合并到 `dst` token 上 ## `merge()` ### 函数声明 ```python # 定义合并函数:把选中的 src 汇聚到对应的 dst(默认 reduce=mean),并返回拼接结果 def merge( x: torch.Tensor, mode: str = "mean", extra_tensors=None, # 额外同步合并的 tensor,保证后续 q@k 的序列长度一致。 extra_tensors_2=None, # 额外同步合并的 tensor 2,同上 ) -> Union[ torch.Tensor, Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], ]: ``` Function call (in `attention.py`): ```python q_merge_in = q.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) k_merge_in = k.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) v_merge_in = v.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_q, N_q, H_q * D_q) q_out, k_out, v_out = m_a( q_merge_in, mode="mean", extra_tensors=k_merge_in, extra_tensors_2=v_merge_in, ) ``` ### 具体实现 ```python # 按与 metric 相同的分割策略拆分 x if enable_protection: src, dst, protected = split(x) else: src, dst = split(x) n, t1, c = src.shape # 未合并的 src:根据 unm_idx 取出保留的 src 片段 unm_len = unm_idx.shape[1] unm = gather(src, dim=-2, index=unm_idx.expand(n, unm_len, c)) # 待合并的 src:根据 src_idx 选出前 r 个 src_len = src_idx.shape[1] src = gather(src, dim=-2, index=src_idx.expand(n, src_len, c)) # 将待合并的 src 聚合到对应的 dst;mode 默认为 mean,可改为 sum 等 dst = dst.scatter_reduce(-2, dst_idx.expand(n, src_len, c), src, reduce=mode) ``` 后面 `extra_tensors / extra_tensors1` 的流程是一样的。 ## `unmerge()` ```python # 先按顺序切分短序列:未合并 src(unm)、聚合后 dst、(可选)protected unm_len = unm_idx.shape[1] dst_len = num_dst src_len = src_idx.shape[1] unm = x[..., :unm_len, :] dst = x[..., unm_len : unm_len + dst_len, :] if enable_protection: protected = x[ ..., unm_len + dst_len : unm_len + dst_len + num_protected_actual, : ] # 用 dst 的聚合结果反向还原被合并的 src:根据 dst_idx 把 dst 拷回合适位置 _, _, c = unm.shape src = gather(dst, dim=-2, index=dst_idx.expand(B, src_len, c)) # 准备完整输出,并逐块 scatter 到原始索引位置 out = torch.zeros(B, N, c, device=x.device, dtype=x.dtype) # 1) 把 dst 放回原来的 b_idx(目标侧)位置 out.scatter_(dim=-2, index=b_idx.expand(B, num_dst, c), src=dst) # 2) 把未合并的 src 放回 a_idx 对应的 unm_idx 位置 out.scatter_( dim=-2, index=gather( a_idx.expand(B, a_idx.shape[1], 1), dim=1, index=unm_idx ).expand(B, unm_len, c), src=unm, ) # 3) 把被合并的 src(从 dst 反向恢复出来的片段)放回 a_idx 对应的 src_idx 位置 out.scatter_( dim=-2, index=gather( a_idx.expand(B, a_idx.shape[1], 1), dim=1, index=src_idx ).expand(B, src_len, c), src=src, ) # 4) 若启用保护,将 protected 片段 scatter 回 protected_idx 对应位置 if enable_protection: out.scatter_( dim=-2, index=protected_idx.expand(B, num_protected_actual, c), src=protected, ) return out ``` ## `fast_similarity_chunks()` ### 函数声明 ```python def fast_similarity_chunks( a: torch.Tensor, b_transposed: torch.Tensor, chunk_size: int ) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]: ``` Function call: ```python node_max, node_idx = fast_similarity_chunks(a, b_transposed, chunk_size) ``` ### 具体实现 注:`torch.bmm` 的全称是 **batch matrix-matrix product**,也就是 **批量矩阵乘法**。它一次性对一批(batch)里的多个矩阵做乘法运算。 - 输入:两个三维张量 `input` 和 `mat2` - 形状分别是 `(b, n, m)` 和 `(b, m, p)` - 输出:三维张量,形状是 `(b, n, p)` 其中 **`b`** 表示 batch size,也就是一批里有多少个矩阵要相乘。 每个 batch 内对应位置的矩阵会被相乘。 核心代码: ```python # Process in chunks for i in range(0, num_src, chunk_size): end_i = min(i + chunk_size, num_src) a_chunk = a_bf16[:, i:end_i, :] # [B, chunk_size, C] scores_chunk = torch.bmm(a_chunk, b_transposed_bf16) # 由于外层已对 a、b 做 L2 归一化,点积近似余弦相似度 chunk_max_bf16, chunk_idx = torch.max(scores_chunk, dim=2) # 在每个 src 行上找出最大值及其列索引(对应某个 dst chunk_max = chunk_max_bf16.to(original_dtype) node_max[:, i:end_i] = chunk_max node_idx[:, i:end_i] = chunk_idx return node_max, node_idx ``` ## 总结 1. 如果考虑要修改 protected token 的代码,那么所有 `enable_protection` 的代码都应该被考虑修改 2. ... 最后修改:2025 年 09 月 29 日 © 允许规范转载 打赏 赞赏作者 支付宝微信 赞 如果觉得我的文章对你有用,请随意赞赏